Purified water isn’t just H₂O, there’s more happening beneath the surface. Invisible gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen dissolve into the water, influencing everything from its pH to its ability to corrode metal. Ever wondered why soda fizzes, why some water affects industrial equipment, or why certain gases are added to beverages? The answer lies in dissolved gases. In this article, we’ll discuss several types of dissolved gases, how they interact with purified water, and how they affect different applications.
What Are Dissolved Gases?
Dissolved gases are physically trapped within a liquid, like water. In industrial operations, they can enter water through natural processes such as atmospheric contact, pressure changes, or intentional dissolution. For instance, CO₂ dissolving in water forms carbonic acid, which impacts the water’s pH.
Types of Gases Dissolved in Purified Water
Dissolved gases in purified water can vary, but they typically include:
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
CO₂ dissolving in water is a well-known example of gas dissolved in a liquid. It reacts with water to form carbonic acid, which lowers the pH. This process is crucial in beverage production (e.g., sparkling water) and treatment.
Oxygen (O₂)
Dissolved oxygen is necessary in biological systems, such as supporting aquatic life, but its presence in purified water used in industrial settings can cause corrosion of metal surfaces.
Nitrogen (N²)
Although relatively inert, nitrogen gas soluble in water reduces the oxygen concentration, which can benefit corrosion control.
Hydrogen (H₂)
Hydrogen is used in specialized applications, such as in creating hydrogen-enriched water for potential health benefits.
Each of these gases reacts differently with water and can have various effects depending on the circumstances. Explore the differences between various water types to understand their impact better.
Effects of Dissolved Gases in Purified Water
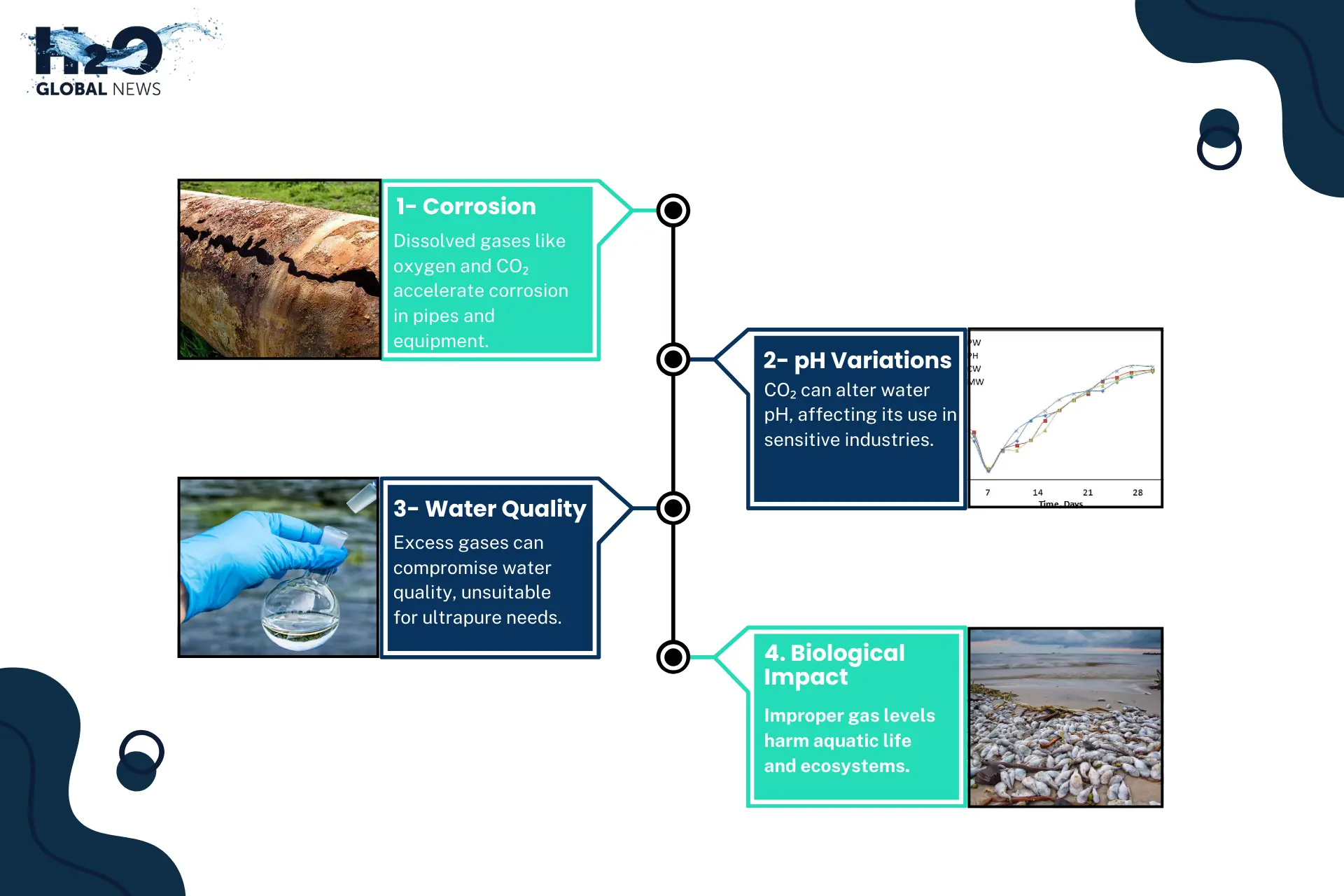
1- Corrosion
The mixture of gas in the water, notably oxygen and carbon dioxide, increases the corrosion of pipes, storage tanks, and other equipment. This is particularly problematic in industrial and laboratory environments.
2- pH Variations
Chemical reactions between gas and water mix, particularly CO₂, can modify the pH of purified water, impacting its appropriateness for purposes such as pharmaceuticals and electronics production.
3- Impact on Water Quality
High quantities of gases, such as CO₂ and N₂, can introduce reactive components into water, compromising its cleanliness. Polish water with gas commonly contains CO₂, suitable for carbonated beverages but unsuitable for ultrapure water requirements.
4- Effect on Biological Systems
Dissolved gases, such as oxygen, are essential for aquatic organisms. However, overly high or low concentrations can harm these ecosystems.
Advanced oxygenation methods can significantly enhance water quality in aquaculture, improving the sustainability of aquatic environments.
Applications of Dissolved Gases
Beverage Industry
In carbonated drinks, CO₂ dissolving in water creates the fizziness we associate with sparkling beverages like soda and polished water with gas.
Industrial Processes
Dissolved gases are controlled to prevent corrosion or unwanted chemical reactions in industries like power generation and semiconductors.
Scientific Research
In laboratory settings, the presence or absence of certain dissolved gases can significantly impact experiments. For example, removing oxygen can prevent oxidation reactions.
Examples of Dissolved Gases
Here are some gas dissolved in a liquid examples to illustrate their role in daily life:
- CO₂ in carbonated beverages
- Oxygen in natural water bodies
- Nitrogen in beer for a creamy texture
- Hydrogen in hydrogen-enriched water
Another interesting example of gas dissolved in a gas is the atmosphere, where nitrogen and oxygen are mixed with trace amounts of other gases.
Conclusion
Dissolved gases influence the chemical and physical properties of purified water. While some gases, such as oxygen and nitrogen, naturally occur, others, such as carbon dioxide, may be artificially supplied for specialized reasons.
Understanding the behavior of gas dissolved in a liquid is essential for industries, scientific research, and even everyday use. Whether it’s ensuring the quality of Polish water with gas or controlling corrosion in pipelines, managing dissolved gases is vital for optimizing the benefits of purified water.
FAQs
1. When Gas and Water Mix, What Happens?
When gas dissolves in water, it forms a homogeneous solution. The extent of dissolution depends on factors like pressure, temperature, and the gas’s solubility.
2. Is Hydrogen Gas Soluble in Water?
Yes, hydrogen is slightly soluble in water, but its solubility is lower than that of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
3. Why Is Dissolved Gas Important in Purified Water?
Dissolved gases can influence purified water’s pH, conductivity, and chemical reactivity, affecting its use in sensitive applications.