Wastewater management is a complex system that safeguards the environment and public health behind every flush, wash, and drain. This crucial procedure, sometimes disregarded, guarantees that water is cleaned and safely reintroduced into the environment. In this article, we’ll cover the definition of wastewater, the importance of all stages of wastewater treatment, and the overall effects of wastewater management on natural resources.
What is Wastewater?
Any water utilized and contaminated by human activities is simply called wastewater. This comprises stormwater runoff, industrial, agricultural, and residential water. It frequently contains contaminants, including chemicals, organic waste, and pathogens, that must be eliminated before the water is released into the environment.
What is Wastewater Treatment?
Wastewater is treated in specialized facilities to protect the environment and public health. This procedure purges impurities from water so that it is safe to reuse or release. Specific methods are necessary for a water management system to be thorough.
What is Wastewater Management?
A water management system includes wastewater collection, treatment, and safe disposal or reuse. So, what is wastewater management? It’s a thorough strategy that addresses sustainability and water quality by combining technology, legislation, and neighborhood initiatives.
Effective wastewater management reduces pollution and promotes water conservation by recycling treated water for industrial use, groundwater replenishment, or irrigation.
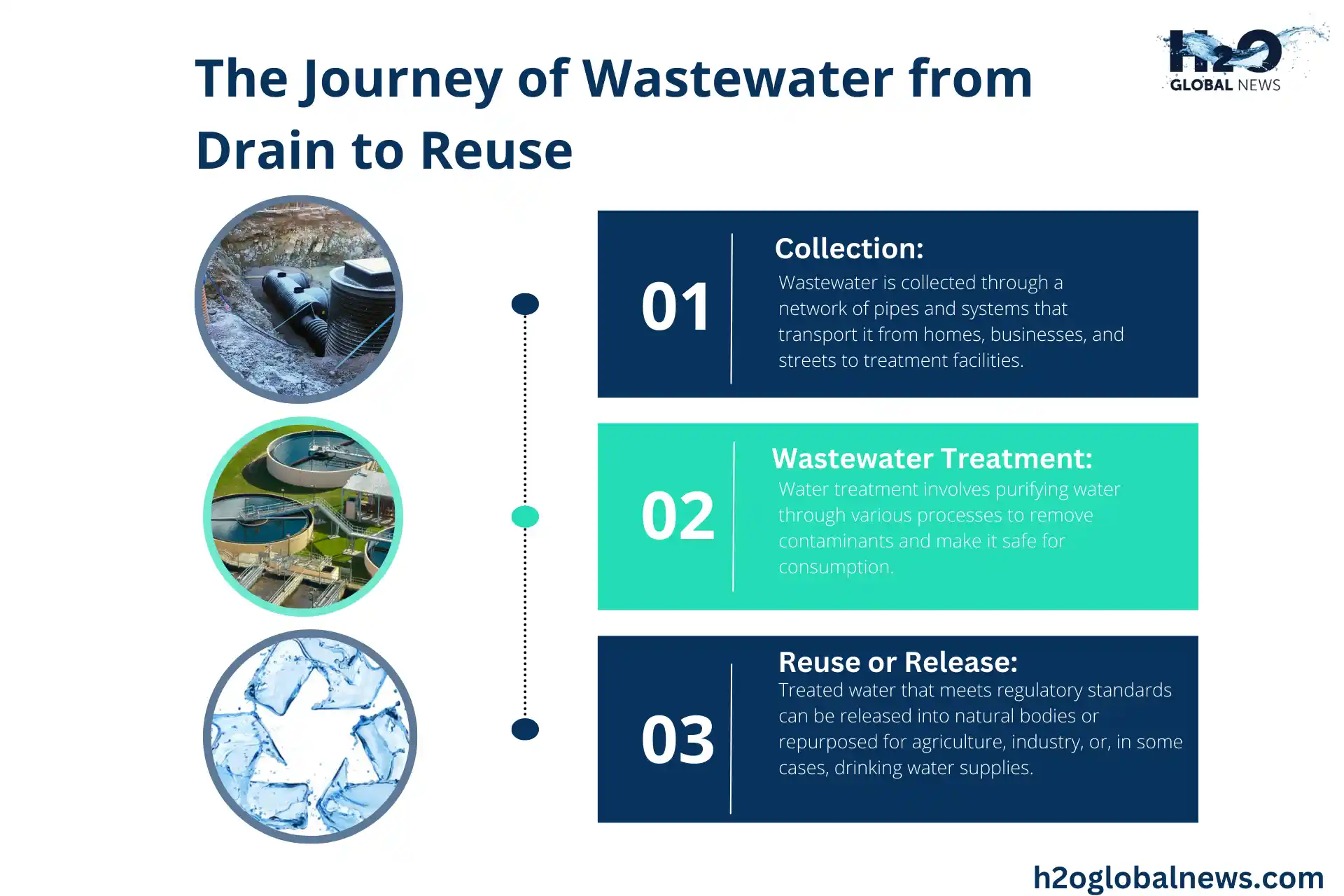
The Journey of Wastewater from Drain to Reuse
The path wastewater takes from being considered waste to potentially reusable water is a testament to human ingenuity and our efforts to live harmoniously with the environment. Here’s a broad overview of this fascinating process:
1. Collection
Wastewater begins its journey by being collected via a vast network of pipes and conveyance systems designed to transport it safely from homes, businesses, and streets to treatment facilities.
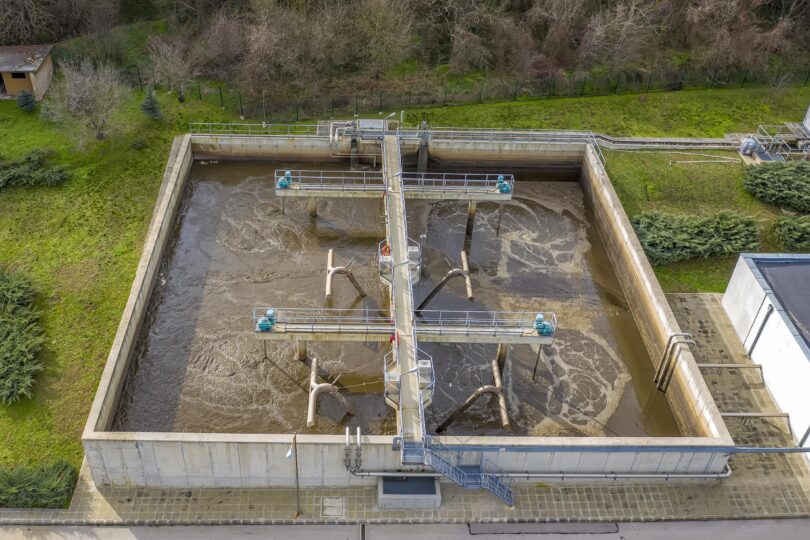
2. Wastewater Treatment Stages
Upon arriving at a wastewater treatment plant, the water undergoes several treatment stages designed to remove contaminants and make the water suitable for release back into the environment or reuse. These stages generally include:
- Preliminary Treatment: Removal of large solids and debris through screening and grit removal.
- Primary Treatment: Sedimentation processes that allow organic solids to settle and be removed.
- Secondary Treatment: Biological processes that break down dissolved organic matter not removed during primary treatment.
- Tertiary Treatment: Advanced treatment processes that further improve water quality by removing remaining inorganics and nutrients, often involving filtration and disinfection methods.
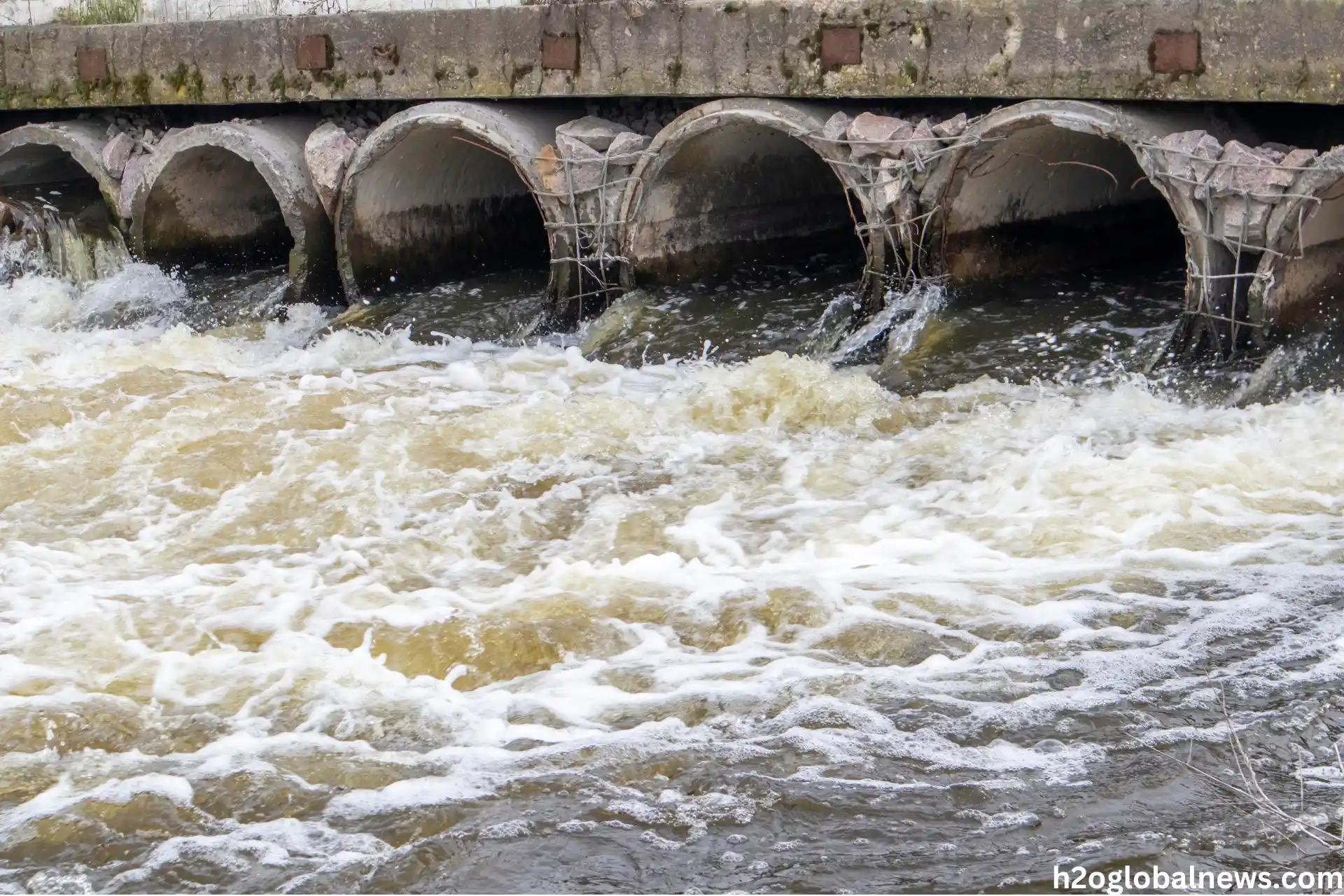
3. Reuse or Release
Treated water that meets regulatory standards can then be released back into natural water bodies, such as rivers or seas, or repurposed for various uses, including agricultural irrigation, industrial processes, or, under certain conditions, replenishing drinking water supplies.
The Importance of Wastewater Management
Wastewater management is crucial for several reasons:
- Protecting Public Health: Proper wastewater treatment eliminates disease-causing organisms and hazardous substances, preventing waterborne diseases.
- Environmental Conservation: By treating and adequately disposing of wastewater, we protect water quality in rivers, lakes, and oceans, safeguarding aquatic ecosystems and wildlife.
- Water Scarcity Solutions: Advanced treatment and reuse technologies can make wastewater a valuable resource in water scarcity regions, contributing to sustainable water management practices.
- Economic Benefits: Effective wastewater management supports industries, agriculture, and communities by providing a reliable water source and reducing the costs associated with environmental degradation and health care.
How Does Wastewater Treatment Impact Natural Resources?
Proper treatment maintains water quality in rivers, lakes, and oceans, guaranteeing the health of aquatic ecosystems. Reusing treated water also helps promote sustainable development by lessening the demand for freshwater resources.
Conversely, poorly managed wastewater can result in pollution, biodiversity loss, and health problems. Therefore, wastewater treatment is essential to environmental preservation.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its critical role, wastewater management faces numerous challenges, including aging infrastructure, increasing population pressures, climate change impacts, and emerging contaminants. Addressing these challenges requires innovation, investment, public water conservation, and pollution prevention education.
As we look to the future, technological advances offer promising solutions for more efficient and sustainable wastewater treatment. The potential for innovation in this field is vast, from energy-generating treatment processes to innovative water management systems. By supporting these developments and recognizing the value of wastewater as a resource, we can ensure the continued protection of public health, the environment, and the global economy.
Conclusion
An unseen but essential component of contemporary society is wastewater management. We can grasp the enormous significance of this process by knowing what wastewater is, what wastewater treatment is, and what a water management system does. In addition to protecting the environment, proper management and guarantee of therapy that water resources are used sustainably for generations.
The function of wastewater treatment stages and their effects on natural resources become increasingly crucial as the world experiences growing water scarcity. Creativity and consciousness can create a future where water is valued, conserved, and reused.
Read the latest wastewater news.
FAQs
What are the different types of wastewater?
Wastewater can be divided into four categories: domestic, industrial, agricultural, and stormwater runoff, all of which carry different contaminants and pollutants.
What are the most common pollutants found in wastewater?
Common pollutants—including organic waste, chemicals, heavy metals, nutrients, and pathogens—threaten human health and the environment.
How does wastewater treatment impact energy consumption?
Wastewater treatment can be energy-intensive and climate-polluting, but innovations such as energy recovery systems aspire to lower their carbon footprint and energy demand.