Water scarcity is becoming a growing concern around the world, especially in areas with limited access to fresh water sources. One smart solution that is gaining attention is fog harvesting. This method uses natural fog to collect water and provides a useful alternative in areas where traditional water sources are hard to access. To help you better understand, let’s discuss fog harvesting, its workings, and its benefits in water shortage areas.
What Is Fog Harvesting?
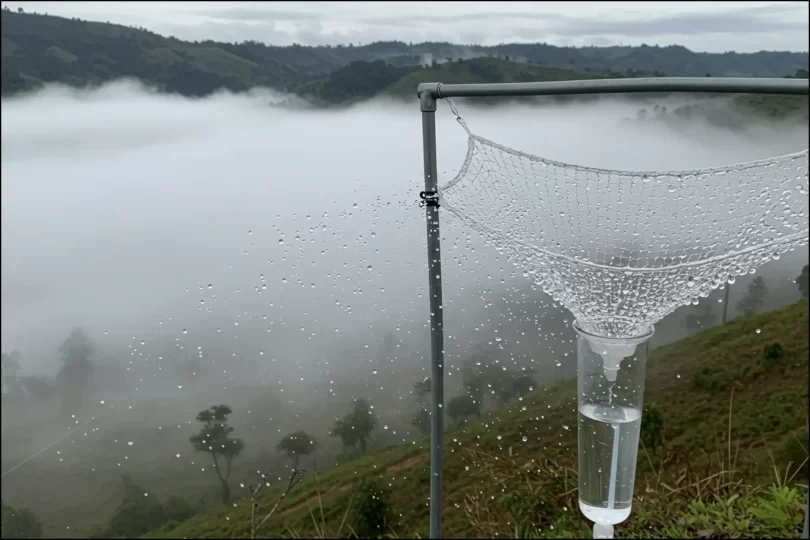
Fog harvesting is a method used to collect water from air fog. Fog is made up of tiny water droplets that float in the air. It is especially useful in places where the air is humid but rainfall is low. These are often coastal regions, deserts, or mountain areas where fog forms regularly but rain doesn’t fall often. According to studies, about 800 million people worldwide do not have access to drinking water. That’s why many places now harvest fog to meet basic water needs.
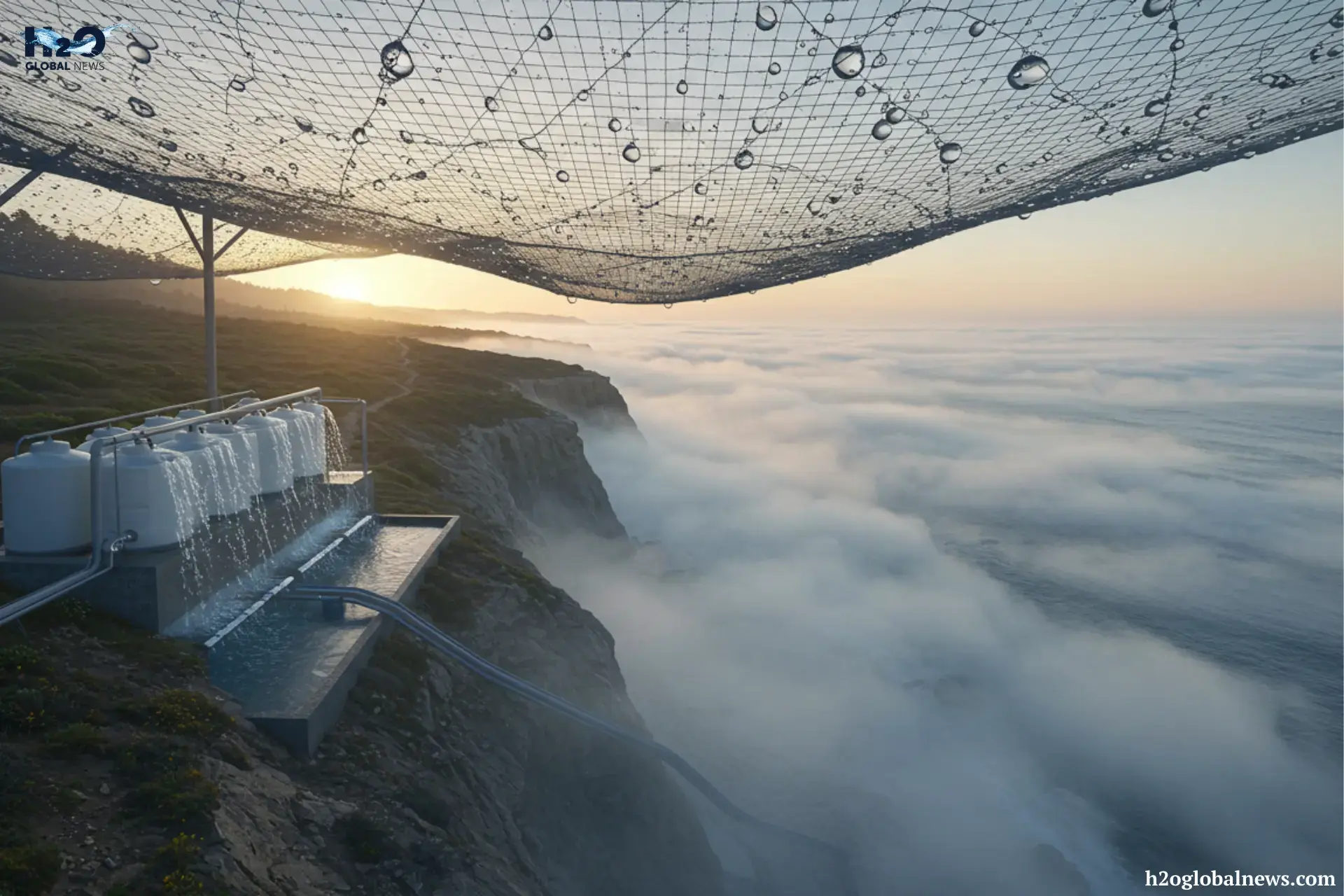
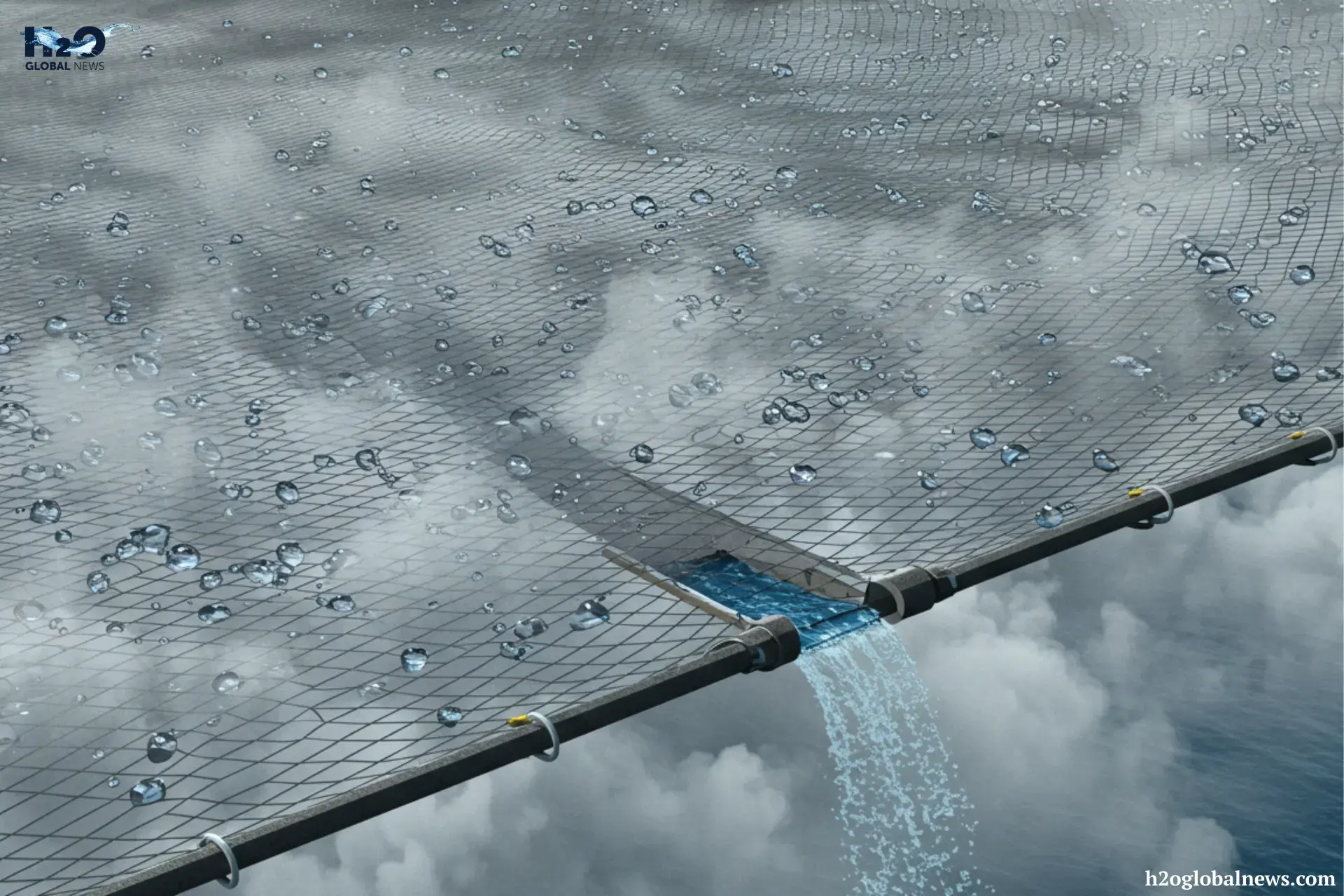
People use special mesh nets, often called fog collectors, to collect water that stands in the path of moving fog. When fog passes through the net, the droplets stick to the surface, gather together, and eventually drip into a container below. This clean, collected water can then be used for drinking, farming, and more.
How Does the Fog Harvesting System Work?
Harvesting water from fog doesn’t require electricity or machines; it just requires fog, wind, and specially designed nets. Here’s how this system works:
1- Mesh Nets
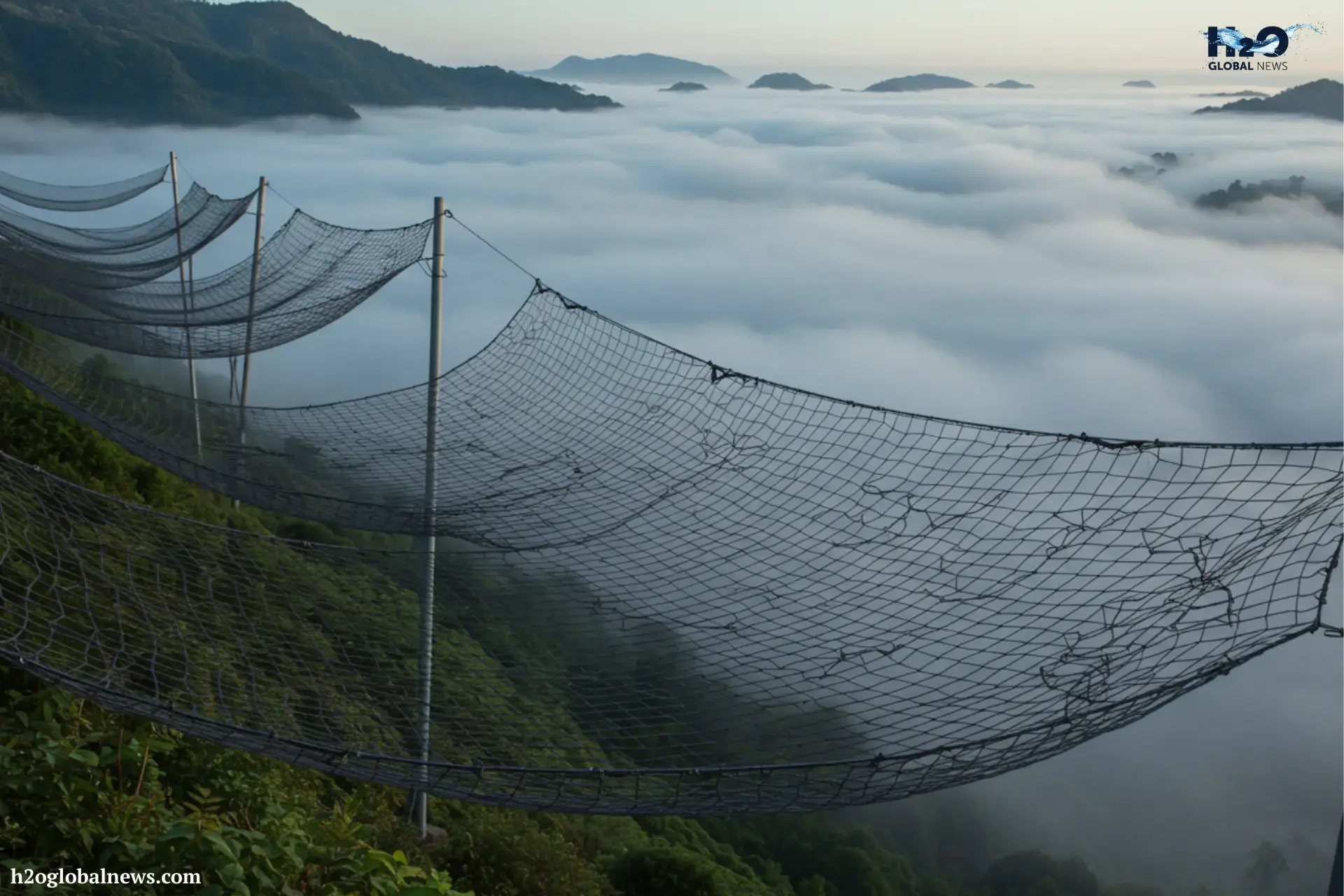
The main part of a fog harvesting system is large vertical mesh nets, often made of materials like polypropylene or nylon, to harvest fog. These materials are strong, weather-resistant, and good at catching tiny water droplets. The holes in the net are just the right size, not too big, not too small, so water can stick to them as fog passes through. In the Atacama Desert (one of the driest places on Earth), scientists estimate that fog nets produce up to 10 liters of water per square meter daily.
2- Condensation Process
When fog moves through the mesh, the tiny water droplets in the fog hit the net and stick to the fibers. Once they’re stuck, they start to join together and grow into larger drops. As the drops become heavier, they drip down due to gravity. A small gutter or pipe placed below the net catches the dripping water and channels it downward. Studies have shown that a single square meter of fog net can produce 2 to 5 liters of water under good fog conditions.
3- Filtration
After the water drips off the mesh, it flows into collection tanks. The tanks store the harvested water until it’s ready to use. Before the water is used for drinking, it usually passes through a basic filtration system to remove dirt, dust, or tiny particles. In some setups, the water may be treated or boiled with UV light to make it even safer.
Benefits of Fog Harvesting
It offers several key benefits that make it an attractive solution, especially in regions with insufficient water resources. Here are some of the reasons why this is the best option:
1- Good Water Source
It provides a renewable source of water in areas where natural freshwater is hard to come by. Since fog is a natural occurrence, it doesn’t require the extraction of groundwater or reliance on expensive infrastructure, which makes it a sustainable option for long-term water needs.
2- Low-Cost Infrastructure
Fog harvesting systems are relatively simple to set up and maintain compared to other water collection systems like wells or desalination plants. The materials used (like polyethylene mesh and simple collection tanks) are affordable, and the energy requirements are minimal, mostly relying on natural fog, which costs nothing.
3- Reduces Water Scarcity
It can play an important role in reducing water scarcity in coastal or mountainous regions where conventional rainfall is insufficient, yet fog occurs frequently. For example, in Morocco, the Boutmezguida project captures around 6,000 liters of water per day, which is used by local villages and for agricultural purposes.
4- Improves Local Agriculture
In dry regions where irrigation is a challenge, harvesting water can help support local agriculture. The water collected can be used for irrigation or even to hydrate livestock. This is beneficial for communities that depend on farming or pastoralism and can grow food or feed animals, which increases local food security.
5- Minimal Environmental Impact
Unlike other water harvesting methods like desalination, which can use up to 15,000 kWh per million gallons of water produced, this has a very low environmental impact. It doesn’t require the burning of fossil fuels or the disturbance of local ecosystems.
6- Works well with Climate Change
As climate change increases the unpredictability of weather patterns, it offers a stable water source that is not at risk of droughts or changing rainfall patterns. Even in drought-prone areas, fog may still occur regularly, which makes it a reliable option in a changing climate.
Innovations in Fog Harvesting Technology
Researchers and engineers are continuously improving fog harvesting systems:
- Bioinspired Meshes: New net designs mimic beetle shells or spider webs, which are naturally efficient at collecting moisture.
- Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic Coatings: Enhancing water droplet formation and runoff speed.
- AI-Powered Fog Forecasting: Used to predict peak fog periods for better water collection timing.
These advancements are helping to make fog harvesting more efficient, affordable, and scalable.
Conclusion
Fog harvesting is a smart and natural way of gathering water, especially in places where other sources are hard to find. It’s clean, simple, and helps people capture water from air. Whether it’s for drinking, farming, or washing, you should know that harvesting water from fog could make a huge difference for the future. It shows us that even a quiet mist in the air can become something life-changing.
FAQs
1- Can the water from fog harvesting be used for drinking?
Yes, water collected from fog harvesting is usually filtered to remove dust, dirt, and small particles before being used for drinking.
2- Is fog harvesting used globally?
Yes, fog is used in several parts of the world, including coastal regions of Chile, Morocco, and parts of South Africa, as well as areas in the Middle East and Asia, where fog is common.
3- How much does a fog harvesting system cost?
It depends on size and material, but basic systems can be set up for a few hundred dollars and can last for years.
4- Is fog harvesting better than rainwater harvesting?
It depends on your location. If you get fog regularly but little rain, fog water harvesting might be a better choice.