We drink water every day, and it is one of the first things we trust to keep us healthy. But the quality of water matters; sometimes, we get hard water, which can affect our health and our household appliances.
If you notice white marks on your taps, a strange taste in your water, dryness on your skin after showering, or limescale buildup in your kettle, you are probably dealing with hard water.
With so much online information, it’s natural to feel a bit concerned and confused. One common question is, “Is hard water safe to drink?” To help you understand all about drinking hard water, we have researched and compiled a guide to help you determine whether hard water is safe to drink or not.
We’ve discussed water hardness, its pros and cons, how it impacts your body, and how to test and treat it in your home. By understanding this, you can easily identify hard water in your home and know how it could affect your health.
What is Hard Water?
Hard water contains high levels of minerals, especially calcium and magnesium, which are naturally occurring minerals. These minerals get into the water naturally when it flows through rocks and soil, especially in areas with limestone. The higher the concentration of these minerals, the “harder” the water becomes.
It can affect your household in various ways, such as leaving white limescale on taps, reducing soap’s effectiveness, and even shortening the life of appliances like kettles and washing machines.
In the United States, the USGS reports that the country has lots of hard water, with particularly high levels in states like Texas, Arizona, Florida, and Indiana.
You can measure how hard your water is by using the water hardness scale, which classifies water as soft, moderately hard, hard, or very hard according to the amount of minerals in it. It’s usually measured in milligrams per liter (mg/L) or grains per gallon (gpg). According to the U.S Geological Survey:
| Soft water | 0-60 mg/L of minerals |
| Moderately hard water | 61-120 mg/L |
| Hard water | 121-180 mg/L |
| Very hard water | Over 180 mg/L |
Hard water differs from soft water because of the level of minerals in it. Hard water has a high level of minerals, but soft water has low levels. Soft water doesn’t cause limescale, allows soap to lather easily, and is generally gentle on your skin, hair, and appliances.
Common Signs of Hard Water
If you are not sure that you have hard water at home, here are some signs. You may have to check your water hardness levels if you notice these signs.
- White, chalky residue on dishes and glassware
- Dry, itchy skin after bathing
- Stiff and rough laundry even after washing
- Soap and shampoo don’t lather well
- Buildup around faucets and showerheads
- Appliances like kettles and water heaters develop scale deposits
How to Test Water Hardness at Your Home?
- Fill a bottle halfway with water, add a few drops of liquid soap, and shake it. If there’s little lather and more cloudy residue, your water is likely hard.
- You can also buy a hard water test kit, which can provide quick results based on the mineral concentration in your water.
- For more accuracy, you can contact your water supplier to know the levels for your area.
Is Hard Water Safe to Drink?
Yes, hard water is generally safe to drink. Many health authorities, including the World Health Organization (WHO), confirm that there’s no health risk associated with drinking hard water. The minerals found in hard water, mainly calcium and magnesium, are actually essential nutrients that your body needs.
There is a common myth that minerals in hard water are contaminants. They’re actually naturally occurring nutrients that can be beneficial to your health. According to studies, hard water may even contribute small amounts of dietary calcium and magnesium, supporting bone health and heart function. While the mineral content varies from region to region, it’s not considered harmful or dangerous in normal levels.
Health Effects of Hard Water
Hard water is not harmful to drink in minor quantities. It can even offer a few health benefits. The minerals in hard water, mainly calcium and magnesium, are actually important nutrients your body needs. But there are some health concerns also.
Pros of Drinking Hard Water
Hard water is just one of the many types of water we use daily. Some benefits of using Hard Water are:
1- Rich in Minerals
Hard water can help increase your daily intake of calcium and magnesium, which are vital for your health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), drinking water can provide 5%-20% of your daily magnesium and calcium intake.
Calcium is necessary for strong bones and teeth, and it also plays a key role in your heart and muscle functions. While Magnesium helps regulate blood pressure, supports your immune system, and even helps manage your blood sugar levels.
2- Good for Heart Health
Some studies suggest that consuming magnesium-rich water may reduce the risk of heart disease. According to one study, areas with higher magnesium levels in water had lower rates of cardiovascular deaths. However, this could also depend on a person’s health status.
Cons of Drinking Hard Water
1- Digestive Issues
For most healthy people, the minerals in hard water aren’t harmful. But for those with sensitive stomachs, kidney issues, or those on mineral-restricted diets, the high mineral content might cause digestive discomfort or extra stress on the kidneys and contribute to stone formation.
2- Skin and hair Problems
Many people report dry skin, itchy scalp, and dull hair when using hard water regularly. The minerals in hard water (especially calcium and magnesium) can leave a residue or spots on your skin and hair after showering, which makes it harder for soaps and shampoos to rinse off properly.
Hard water can clog skin pores, leading to acne or irritation. Hair may also become dry, brittle, and hard to manage. Some people also link hard water with increased hair loss, although there’s limited scientific proof for a direct cause-effect relationship.
3- Damage to Appliances
One of the most well-known drawbacks of hard water is its impact on household appliances and pipes. When hard water is heated or evaporates, it leaves limescale buildup (calcium carbonate deposits) in water heaters, dishwashers, kettles, and plumbing systems.
Over time, this reduces the efficiency and lifespan of appliances, increases energy bills, and leads to more frequent repairs or replacements. It shortens the lifespan of appliances like dishwashers and water heaters by up to 30%. That’s why shifting from hard to soft water can significantly increase the lifespan of your appliances.
Hard water is not considered unsafe for drinking. But if you notice skin irritation, buildup in your appliances, or simply don’t like the taste, you can switch to a water softener or filtered water. People with low immunity may experience digestive issues and heart and kidney diseases.
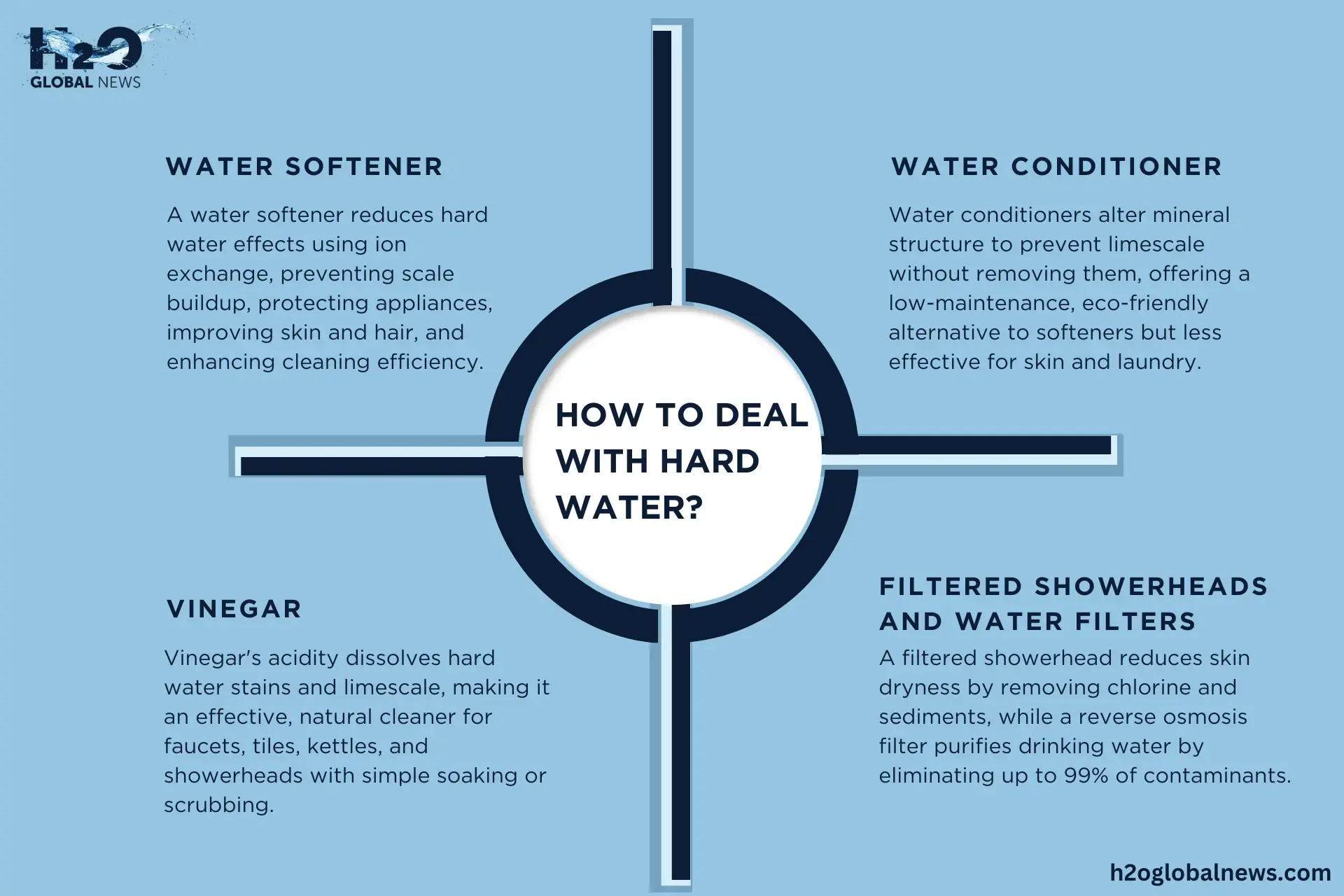
How to Deal with Hard Water?
If hard water is causing trouble in your daily life, such as dull hair, itchy skin, spots on dishes, or limescale buildup in your pipes, you’re not alone. The good news is, that there are several practical ways to manage and reduce the effects of hard water at home.
1- Water Softener
A water softener is one of the most effective solutions for reducing hard water effects on health and protecting appliances. It works using an ion exchange technology, which removes the calcium and magnesium ions and replaces them with sodium or potassium ions.
- This helps reduce scale buildup in pipes and appliances, protects your water heater, and makes water gentler on skin and hair.
- It also helps your soaps and shampoos lather better, which means you have cleaner dishes, softer laundry, and a more pleasant shower experience.
2- Water Conditioner
Water conditioners are a great alternative if you don’t want to use salt or add sodium to your water. They don’t actually remove minerals like a traditional softener does, but instead, they change the structure of the minerals (a process called template-assisted crystallization or electromagnetic treatment) so that the minerals can’t stick to surfaces and form limescale.
These systems are low-maintenance and eco-friendly and work well in reducing scale, though they’re not ideal if your goal is to soften water for skin or laundry.
3- Vinegar
Hard water often leaves behind white chalky stains or crusty limescale on faucets, tiles, kettles, and showerheads. Vinegar is acidic, so it is the best hard water treatment for cleaning scale buildup. You can also use vinegar for regular cleaning to extend the life of your appliances and keep them looking shiny and fresh.
A simple vinegar soak or scrub is a great way to dissolve these mineral deposits. You can soak affected parts in vinegar or spray vinegar directly onto surfaces. Let it sit for 30-60 minutes, then wipe or scrub it clean.
4- Filtered Showerheads and Water Filters
Using a filtered showerhead can make a noticeable difference if you’re dealing with skin dryness or hair issues (and concerning if hard water causes hair loss). These shower filters could help reduce chlorine, sediment, and some hardness minerals in shower water and make it gentle and more skin-friendly.
A reverse osmosis (RO) filter is one of the most effective systems for purifying drinking water. It can remove up to 99% of dissolved minerals and contaminants, such as lead, fluoride, and chlorine.
If you’re concerned about lead contamination, here’s a detailed guide on removing lead from water.
Conclusion
Yes, for most people, it is safe. Hard water is not harmful and even provides beneficial minerals. However, it can cause minor inconveniences like dry skin, hair issues, and appliance damage. If hard water affects your daily life, you can treat it with solutions like installing a softener or using a filter. Understanding your water hardness levels and taking the right steps will guarantee that both your health and home are well taken care of.
FAQs
1- How to fix hard water?
Installing a water softener or using a shower filter can reduce mineral content. For smaller fixes, you can also use vinegar rinses.
2- Can hard water cause breakouts?
Yes, hard water can clog pores due to mineral residue on the skin. This may lead to acne, irritation, or dry, itchy skin for some people.
3- Can hard water cause hair loss?
Hard water doesn’t directly cause hair loss, but mineral buildup can weaken hair and make it brittle over time. This may lead to breakage and dryness.
4- Can hard water cause kidney stones?
No, Hard water doesn’t directly cause kidney stones, but its high calcium content may slightly increase the risk in people already prone to them.