Water is used in various industrial operations, including cooling, cleaning, and direct production. However, not all industrial water is clean and safe for these applications. Industrial water treatment is necessary to ensure that the water used in these operations is safe, efficient, and ecologically friendly. In this post, we will examine industrial water treatment, its components, its importance, and the leading procedures involved.
What is Industrial Water?
Industrial water is used in industrial settings for several purposes, such as cooling, cleaning, processing, and chemical reactions. It can originate from various sources, including surface water (rivers and lakes), groundwater, and municipal supplies. However, industrial water is sometimes unsuitable for direct usage and must be treated to fulfill specific quality criteria before being utilized in manufacturing processes. The water requirements of companies vary greatly depending on the job type, making industrial treatment a highly personalized solution.
Why is Industrial Water Treatment Important?
Several causes contribute to the requirement for industrial water treatment:
- Efficiency: Contaminated water can cause scaling, corrosion, and fouling in equipment, lowering its efficiency and longevity.
- Compliance with laws: Many industries must follow severe environmental laws governing water quality, such as the allowable quantities of contaminants in wastewater.
- Safety: Unclean water can provide a safety risk in specific industrial processes, particularly those involving chemicals or food manufacturing.
- Environmental Impact: Untreated industrial effluent can pollute rivers, lakes, and oceans.
The Industrial Water Treatment Process
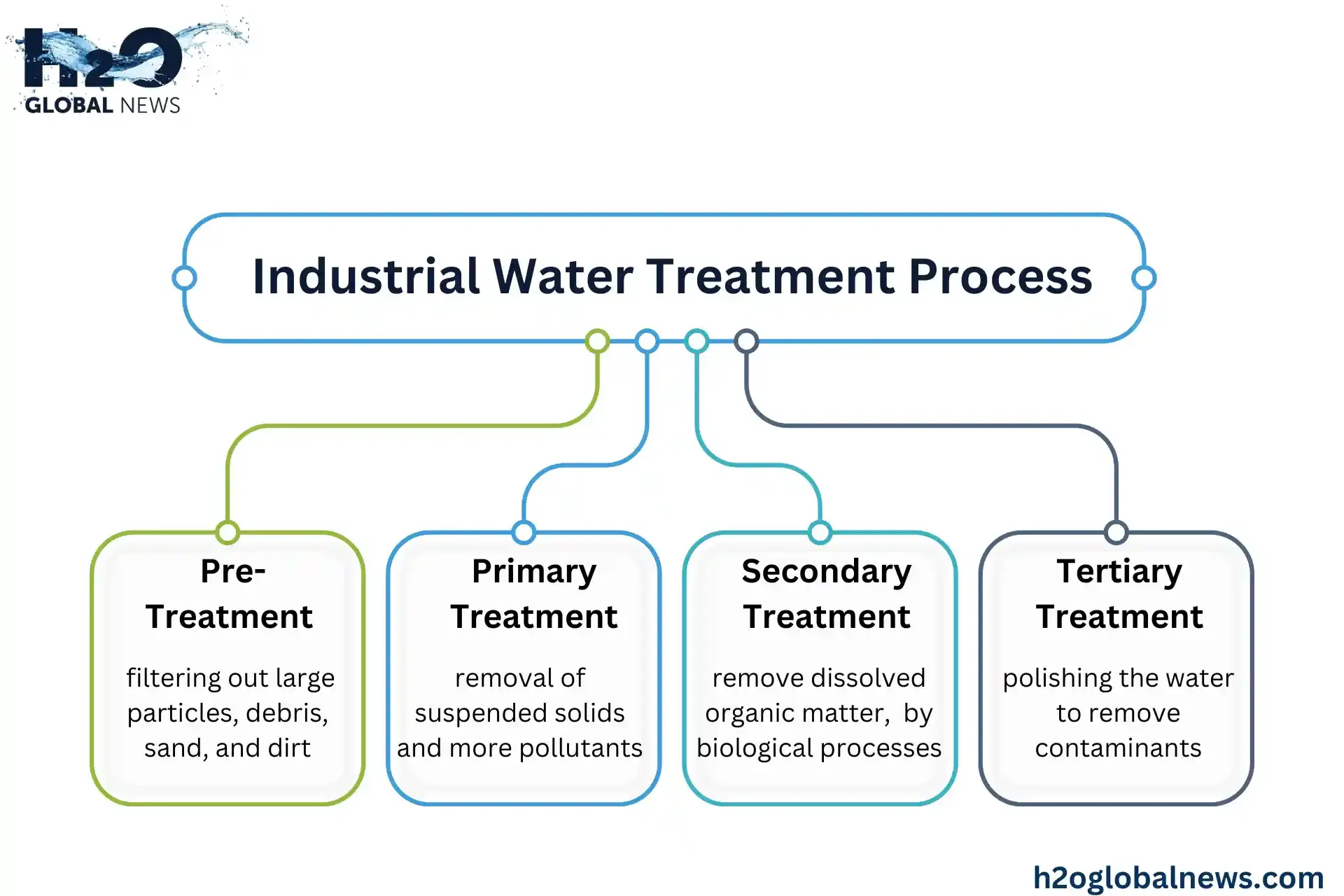
The industrial water treatment process typically involves several stages designed to remove contaminants and impurities from water to make it suitable for industrial applications. Below are the typical steps involved:
1. Pre-Treatment
The first stage in industrial treatment involves filtering out large particles such as debris, sand, and dirt. This may include:
- Coarse filtration: Using screens or mesh to remove large particles.
- Sedimentation: Allowing suspended solids to settle out of the water before further treatment.
- Flocculation: The addition of chemicals to agglomerate particles into larger clusters that can be removed.
2. Primary Treatment
Primary treatment focuses on the removal of suspended solids and more significant pollutants. This can include:
- Gravity separation: Using gravity to separate contaminants.
- Sedimentation tanks: These are used to remove heavier particles from the water.
3. Secondary Treatment
Secondary treatment aims to remove dissolved organic matter, often using biological processes. The most common methods include:
- Biological filtration: Microorganisms are used to degrade organic materials.
- Activated sludge processes: Oxygen is introduced to promote microbial growth, which breaks down organic contaminants.
- Membrane bioreactors: A combination of biological treatment and membrane filtration for advanced purification.
4. Tertiary Treatment
Tertiary treatment focuses on further polishing the water to remove any remaining contaminants, especially those that could affect water quality or be harmful. This can involve:
- Chemical treatment: Add chemicals to neutralize remaining contaminants.
- Filtration: More refined filtration methods, such as reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, remove smaller particles.
- UV treatment: Ultraviolet light is used to disinfect water by killing harmful microorganisms.
Industrial Water Purifiers and Filtration Systems
An industrial water purifier is crucial in ensuring that water used in manufacturing and other industrial applications is safe and high-quality. These purifiers are designed to remove impurities from water through various methods, including:
- Reverse Osmosis (RO): This method forces water through a semi-permeable membrane, removing dissolved salts, organic compounds, and other impurities.
- Ultrafiltration (UF): This method uses a membrane to filter out particles and macromolecules.
- Activated Carbon Filtration: Used for removing chlorine, chloramines, and organic compounds, improving water taste and odor.
- Ion Exchange: A process that removes harmful ions (such as calcium or magnesium) from water, preventing scaling and corrosion in equipment.
Industrial water filtration systems are designed to address specific water quality issues and can be customized to the industrial application’s needs.
Industrial Applications of Water
Water is essential for a variety of industrial purposes, such as:
- Cooling systems: Water is used in cooling towers and heat exchangers to regulate temperatures in power plants, factories, and refineries.
- Cleaning & Sanitation: Water is used in many industries, including food and beverage processing, to clean production equipment and maintain sanitary conditions.
- Processing and Manufacturing: Water is commonly used in chemical reactions, cleaning, and as a solvent in manufacturing processes.
- Power Generation: Water is used in steam boilers in power plants to generate steam for turbines.
Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Industrial wastewater treatment is the process of treating polluted water from industrial operations. This is critical not just for pollution prevention but also for water recycling and reuse in various businesses. Wastewater treatment often includes:
- Sedimentation refers to the removal of solids from wastewater.
- Filtration refers to the removal of tiny particles.
- Chemical treatment is the process of using chemicals to neutralize dangerous pollutants.
- Biological treatment involves using microbes to degrade organic pollutants.
Textile, food processing, and petrochemical industries generate vast amounts of wastewater that must be treated before it is discharged into the environment.
Conclusion
Industrial water treatment is essential for ensuring industries access safe, clean water while limiting their environmental effect. From industrial water purification to wastewater treatment, these operations safeguard industrial equipment and encourage sustainability and environmental compliance. Understanding the significance of each phase in the industrial water treatment process is critical for enterprises that want to optimize their water usage and reduce pollution.
FAQs
1- What is the Role of Industrial Water Filtration?
Industrial water filtration removes impurities, sediments, and harmful chemicals, ensuring that water used in production processes is clean, safe, and efficient.
2- Why is Industrial Water Treatment Necessary?
Industrial water treatment is crucial for ensuring water quality, preventing equipment damage, complying with environmental regulations, and reducing environmental impact.
3- How Does Industrial Wastewater Treatment Work?
Industrial wastewater treatment involves sedimentation, chemical treatment, and biological filtration to remove pollutants from water before it is discharged or reused.