With rising water shortages and increasing utility bills, finding a sustainable solution is more important than ever. What if you could collect free, natural water straight from the sky? Rainwater harvesting allows you to capture and store rain for everyday use, watering plants, cleaning, and even drinking with proper filtration. It’s an easy, cost-effective way to reduce reliance on municipal water while benefiting the environment. In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about rainwater harvesting, from how it works to its major benefits.
What is Rainwater Harvesting?
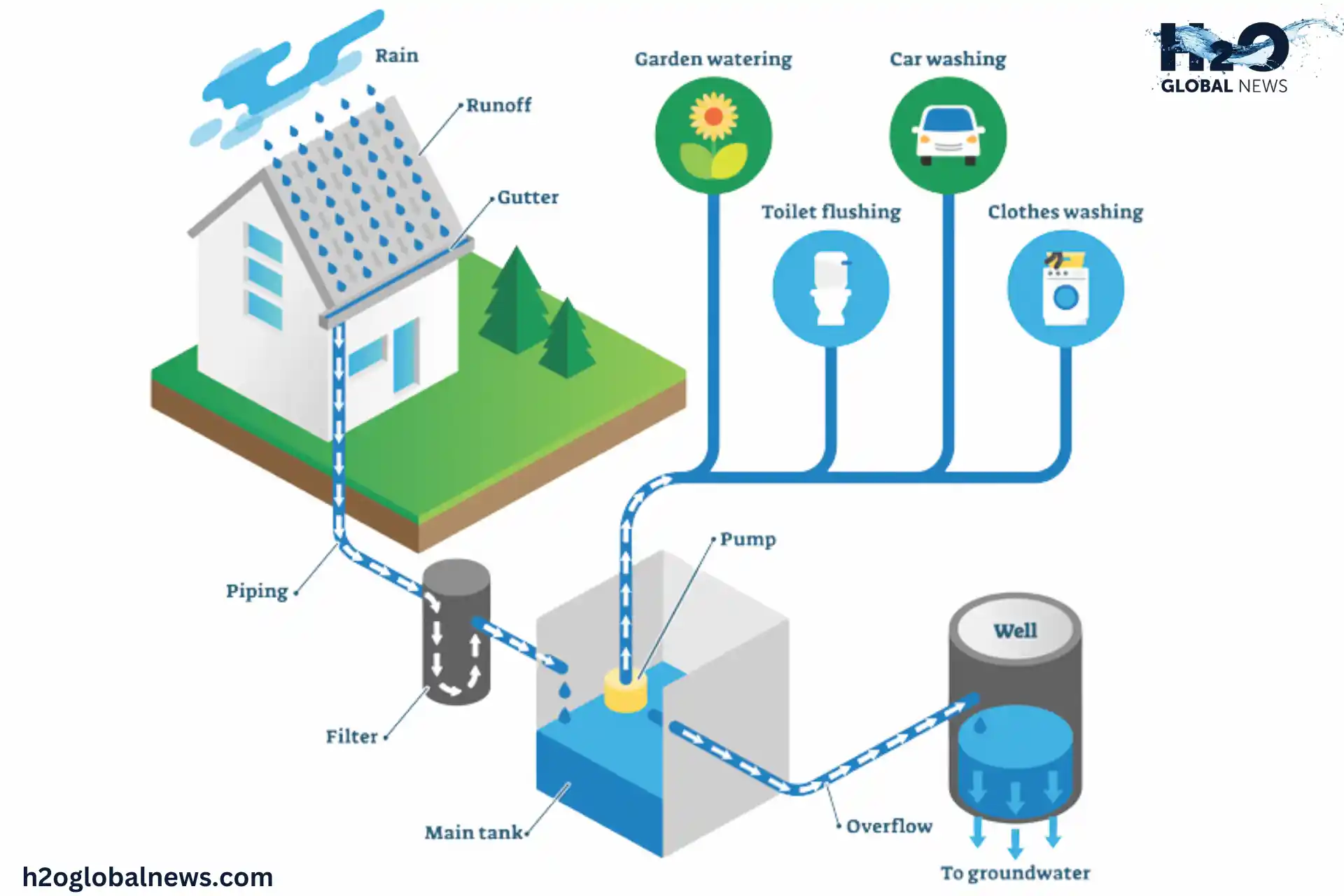
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting rainwater from surfaces such as rooftops, roads, or open fields and storing it for reuse. A rainwater harvesting system typically consists of a catchment area (such as a roof), a conveyance system (pipes), a filter, and a storage unit (such as a rainwater harvesting tank).
After being adequately treated, the collected water can be used for drinking, cleaning, and irrigation. This environmentally friendly technique lessens reliance on municipal water supplies and groundwater. It is an ancient practice that has gained popularity as water conservation methods in agriculture and self-sufficiency have become more important.
Types Of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Active And Passive Harvesting
Active systems use pumps to transfer rainwater from the collection surface to the storage tank, while passive systems rely on gravity. The most common active system uses gutters to transport rainwater from the roof to an above- or below-ground storage tank for residential use. A passive system typically directs rainwater from a catchment surface to an infiltration chamber where it seeps into the soil.
Rainwater harvesting has substantial benefits. It reduces demand on municipal water systems and decreases water bills. It also provides an independent water source in case of water restrictions or disasters. For the environment, rainwater harvesting decreases runoff, recharges groundwater supplies, and reduces pollution from stormwater drains.
To get started with rainwater harvesting, determine your goals and needs. Do you want to water plants, wash laundry, or provide for all household uses? Choose a collection surface, storage tank, and any necessary filtration and pumping equipment. Ensure your system complies with local water use and quality standards regulations. With some upfront investment, rainwater harvesting can provide economical and sustainable benefits for years.
Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
1. Reduces Water Bills
One of the most significant benefits of rainwater harvesting is reducing water bills. Rainwater collection can augment municipal water supplies, lowering water bills for homes and businesses.
2. Preserves Groundwater
Rainwater collection reduces the need for groundwater, helping to restore aquifers and fight water scarcity. This is particularly crucial in drought-prone areas.
3. Reduces Erosion and Flooding
The method reduces excessive runoff, lessens soil erosion, and lessens urban flooding by collecting rainwater.
4. Encourages Sustainable Water Use
Adopting this approach aligns with international initiatives to preserve water and ensure resources are available for future generations.
5. Enhances Plant Development
Rainwater is perfect for irrigation because it doesn’t contain the pesticides and salts frequently present in tap water. This is one of the advantages of rainwater harvesting for agriculture.
6. Reduces Demand on Public Water Systems
Harvested rainwater can ease the strain on municipal water supplies, especially during peak usage periods.
How to Implement a Rainwater Harvesting System
Careful planning and the appropriate parts are needed to set up a rainwater harvesting system:
Step 1: Determine What You Need
Decide how much water you plan to use and collect. This will dictate how your system is designed, including how big the storage tank and catchment area should be.
Step 2: Selecting a Catchment Surface
Roofs are the most typical catchment surface. To gather drinkable rainwater, the surface must be clear and uncontaminated.
Step 3: Installing a Conveyance System
Rainwater can be directed from the catchment area to the storage tank using pipes and gutters. To get rid of debris, install filters.
Step 4: Pick a Tank for Storage
A rainwater harvesting tank must be long-lasting and sized to meet your water requirements. Tanks may be aboveground or underground.
Step 5: Treat the Water
If you plan to use rainwater for drinking or cooking, incorporate a water purification system, such as UV filters or reverse osmosis.
Step 6: Maintain the System
Regularly clean gutters, filters, and tanks to ensure the system functions efficiently and safely.
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting is a practical and sustainable solution to water conservation challenges. Its benefits extend beyond individual savings, contributing to global efforts to manage water resources efficiently. Understanding the benefits of rainwater and implementing simple systems can ensure a more sustainable future for water usage.
FAQs
1- How does a rainwater harvesting system work?
A system collects water from a catchment area, channels it through pipes, filters out debris, and stores it in a tank for future use.
2- Is rainwater harvesting illegal?
Rainwater harvesting is legal and encouraged in most regions. However, some areas have restrictions to protect natural water flow and downstream users.
3- How can I use a rainwater harvesting tank?
After purification, a rainwater harvesting tank stores collected rainwater for irrigation, cleaning, or potable use. Choose a tank size based on your water needs.
4- What are the costs of setting up a rainwater harvesting system?
The cost depends on the size and complexity of the system. Basic setups may cost a few hundred pounds, while more significant, automated systems can cost thousands.
5- How can rainwater harvesting help combat water scarcity?
By reducing demand on municipal water systems and replenishing groundwater, rainwater harvesting contributes to addressing water scarcity challenges.