Water scarcity is a major global issue that affects millions of people and ecosystems. As populations rise and climate change accelerates, water demand continues to outstrip availability, resulting in acute water scarcity in many areas. In this article, we’ll explore the causes of water scarcity, its impact, and most importantly, global freshwater scarcity solutions and solutions to water scarcity that can help combat this growing crisis.
Understanding Water Scarcity
Water scarcity occurs when the water demand exceeds the available supply in a particular region or when water is not accessible or safe for consumption. There are two main types of water scarcity:
Physical Water Scarcity: Occurs when there is not enough freshwater to meet the needs of a population. This is common in arid and semi-arid regions.
Economic Water Scarcity: This happens when people do not have the financial means or infrastructure to access clean water despite the presence of natural freshwater resources.
The Growing Threat of Water Scarcity
Water scarcity is an increasingly dire problem facing communities around the globe. As the population continues to grow, the demand for water rises exponentially while supplies remain limited. Some estimates indicate that by 2025, two-thirds of the world’s population may face water shortages.
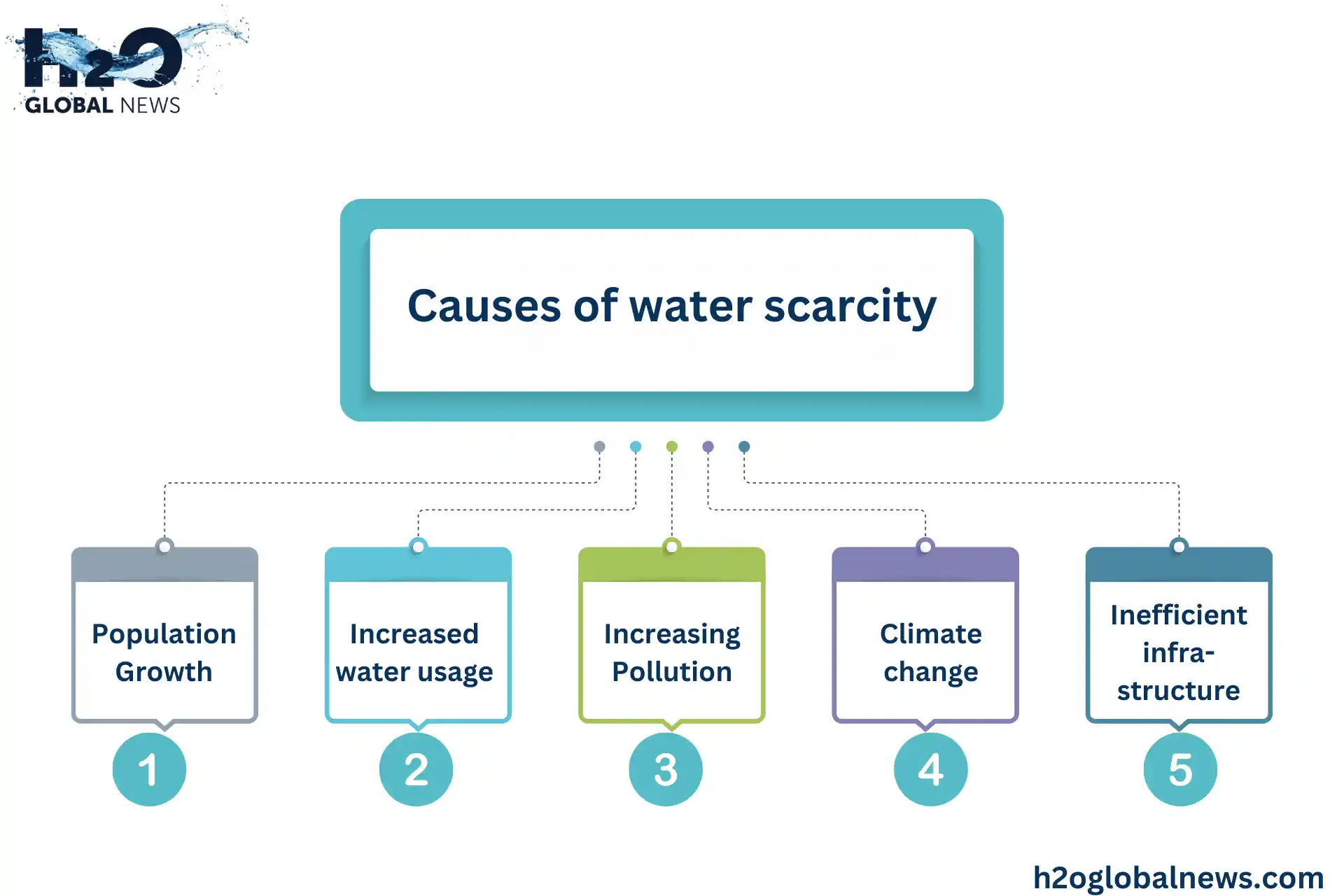
The causes of water scarcity are multifaceted, including:
- Population Growth: As the global population increases, so does the demand for water for drinking, agriculture, and industry.
- Increased water usage: The more people there are, the more water is needed for basic human necessities like drinking, sanitation, and hygiene. Agricultural and industrial activities also require enormous volumes of water.
- Pollution: As water sources become contaminated with chemicals, waste, and pollution, the supply of usable, clean water diminishes. Purifying and treating water requires resources and funds that some communities need more.
- Climate change: Changes in weather patterns are altering precipitation levels and temperatures, which threatens water security. Some areas are experiencing decreased rainfall, while others face more frequent droughts or floods. Glaciers and snowpacks that provide water are melting.
- Inefficient infrastructure: Outdated or poorly maintained water supply systems lead to wasted water through leaks and spills. Improvements in infrastructure and technology can maximize water usage and access.
The Consequences of Water Scarcity
The environment, agriculture, and economic growth are all impacted by water scarcity and human health. Among the most critical repercussions are:
- Health Problems: Every year, thousands of people die from waterborne illnesses, including cholera, dysentery, and typhoid, brought on by a lack of clean water.
- Economic Impacts: Water scarcity results in food insecurity and unstable economies, affecting agricultural sectors, which rely significantly on water for irrigation.
- Environmental Degradation: Aquatic ecosystems suffer from droughts and low water levels, which limit biodiversity.
- Social Unrest: Conflicts can arise from competition for scarce water supplies, especially in tense relations.
Global Freshwater Scarcity Solutions
Policy, behavioral, and technological solutions are needed to address the worldwide water crisis. The following are some of the best ways to address freshwater scarcity worldwide:
Water Recycling and Reuse: Treating and recycling wastewater for non-potable uses like landscaping, industrial cooling, and irrigation can significantly decrease water demand. Some cities have also recycled water for drinking by implementing cutting-edge wastewater treatment systems.
Desalination converts saltwater into freshwater, giving coastal communities a consistent water supply. Although costly and energy-intensive, desalination is becoming increasingly recognized as a practical solution in areas with restricted access to fresh water.
Rainwater Harvesting: In regions with seasonal rainfall, gathering and storing rainwater can be a backup source. This sustainable and economical approach lowers reliance on groundwater or surface water supplies. Collecting rainwater for watering plants and lawns helps conserve municipal water supplies.
Solutions for Water Scarcity
Communities, governments, and people can implement various initiatives to lessen water scarcity. Some workable remedies for water scarcity are listed below:
Effective Water Management: Implementing water-saving techniques like drip irrigation and soil moisture management can increase water efficiency in agriculture. Additionally, water waste can be decreased in metropolitan areas by installing water-efficient appliances.
Water saving Education: Reducing total consumption requires educating the public about water-saving techniques like repairing leaks, taking shorter showers, and adopting water-efficient fixtures.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Agroforestry, better irrigation systems, and drought-resistant crops can all reduce the amount of water used in farming. Thanks to sustainable agriculture, water resources are maintained throughout the food production process.
Better Infrastructure: Modernizing water supply systems to prevent leaks and encourage efficient water distribution can improve access to clean water, particularly in urban areas.
Water Restore: Replenishing Depleted Water Resources
The fight against water scarcity must include the restoration of water resources. Water restoration techniques include:
Groundwater Recharge: Excessive water extraction frequently depletes groundwater levels. Methods like artificial recharge using spreading basins or wells can help restore them.
Wetland Restoration: Wetlands can help ecosystems retain more water by acting as natural water filters. Restoring degraded wetlands can improve water quality, reduce flooding, and provide animal habitats.
Conservation of Forests: Forests are essential to the water cycle because they absorb rainwater and release it gradually. Trees also help preserve natural water sources by preventing soil erosion, which can contaminate water supplies.
Three Sustainable Solutions That Improve Water Quality
It’s crucial to concentrate on enhancing and conserving the available water quality. Three environmentally friendly ways to improve the quality of water are as follows:
Pollution Control: To maintain clean water sources, pollution from industry, agriculture, and urban runoff must be reduced. Enacting stronger laws and encouraging environmentally friendly farming methods can decrease contamination levels.
Wastewater Treatment: Advanced wastewater treatment technologies, such as membrane filtration and reverse osmosis, can remove dangerous chemicals, pathogens, and nutrients from wastewater, making it safe for reuse and lessening the demand for freshwater resources.
Natural Filtration Systems: Before water enters rivers and lakes, pollutants can be naturally removed by creating riparian buffers, wetlands, and biofilters. These eco-friendly alternatives are both economical and sustainable.
Addressing the Water Crisis and Solution
Practical solutions require conservation, technology development, legislative reform, and community involvement. As the situation worsens, investing in short-term and long-term initiatives is crucial to guaranteeing everyone access to safe, dependable, and clean water sources.
Water Crisis Remedies
Among the best solutions for the water shortage are:
International Cooperation: Countries must collaborate to address the global problem of water scarcity and guarantee fair access to water resources, particularly in transboundary water basins.
Empowering Local Communities: By involving local communities in water management, sustainable practices suited to particular areas are promoted, and local knowledge and needs are considered.
Investment in Innovation: To solve future water scarcity, it is essential to keep researching and developing innovative technologies, such as water-efficient farming methods and alternate water sources like desalination.
Conclusion
Water scarcity is an urgent issue that demands immediate attention. While the challenges are significant, the global freshwater scarcity solutions and solutions for water scarcity outlined above offer hope for a more sustainable future. The water crisis can be addressed through innovative technologies, effective water management, and collective action, and future generations will be ensured access to clean, safe, and abundant water.
FAQs
1- How can I help conserve water in my daily life?
You can conserve water by fixing leaks, using water-efficient appliances, taking shorter showers, and reducing water use in landscaping through techniques like xeriscaping.
2- What is the role of technology in solving water scarcity?
Technology is crucial in addressing water scarcity. Innovations like desalination, wastewater treatment, and water-efficient irrigation systems help conserve and restore water resources.
3- How can sustainable agriculture help with water scarcity?
Sustainable agricultural practices such as efficient irrigation, drought-resistant crops, and soil management can significantly reduce water consumption in farming and improve water availability for other uses.