Municipal waste has become a pressing issue worldwide due to its adverse effects on water bodies. Municipalities generate waste from households, businesses, and public spaces, often contaminating water systems. In this article, we’ll explore how municipal waste contributes to water pollution, its impact on aquatic ecosystems, and possible solutions.
What is Municipal Waste?
Municipal or urban waste includes all the rubbish generated by households, businesses, and public institutions within a town or city. This encompasses everything from food scraps and packaging to yard clippings and discarded electronics. Properly managing this waste is crucial to preventing it from becoming a pollutant.
Examples include:
- Household garbage
- Sewage
- Industrial discharge
- Plastic and other non-biodegradable materials
The Breakdown of Municipal Waste
Municipal waste can be divided into several types. Organic waste includes food scraps and yard trimmings. Recyclable materials include paper, plastics, glass, and metals. Hazardous waste contains batteries and chemicals. Finally, residual waste includes non-recyclable and non-biodegradable materials. Understanding these categories is the first step toward effective waste management.
Volume of Waste
The sheer volume of municipal waste produced is staggering. According to the World Bank, the world generates over 2 billion tonnes of municipal solid waste annually. With urbanization on the rise, this number is expected to grow by 70% by 2050. Proper disposal and mana
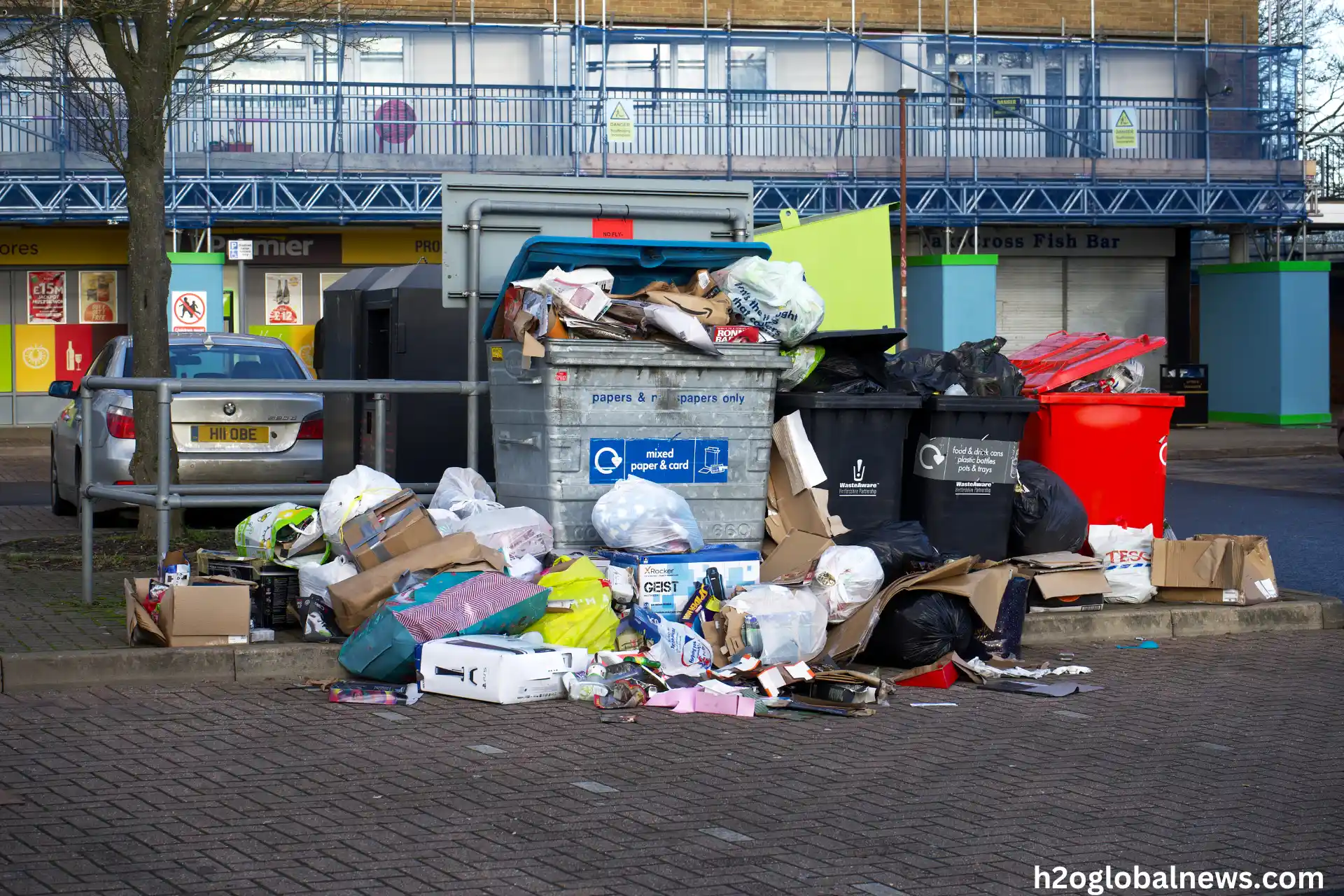
Improper Disposal
Improper disposal of municipal waste leads to significant environmental problems. When waste is not correctly managed, it often finds its way into water bodies through stormwater runoff, illegal dumping, and leachate from landfills. These practices contribute heavily to water pollution, affecting ecosystems and human health.
How Municipal Waste Pollutes Water
1. Improper Waste Disposal
- Dumping trash and H2O waste disposal directly into water bodies is common in some regions.
- Non-biodegradable items like plastics float and accumulate, causing severe pollution.
2. Leachate from Landfills
- Landfills for waste management water can leak harmful chemicals into groundwater.
- These pollutants seep through soil layers, contaminating underground water reserves.
3. Sewage Discharge
- Untreated sewage contains organic matter, pathogens, and nutrients that degrade water quality.
- Without proper municipal wastewater treatment, these pollutants lead to eutrophication, algal blooms, and oxygen depletion.
4. Industrial Effluents
- Factories often release untreated waste into rivers and lakes, contributing to h2o waste pollution.
- Toxic chemicals from industrial discharge can devastate aquatic ecosystems.
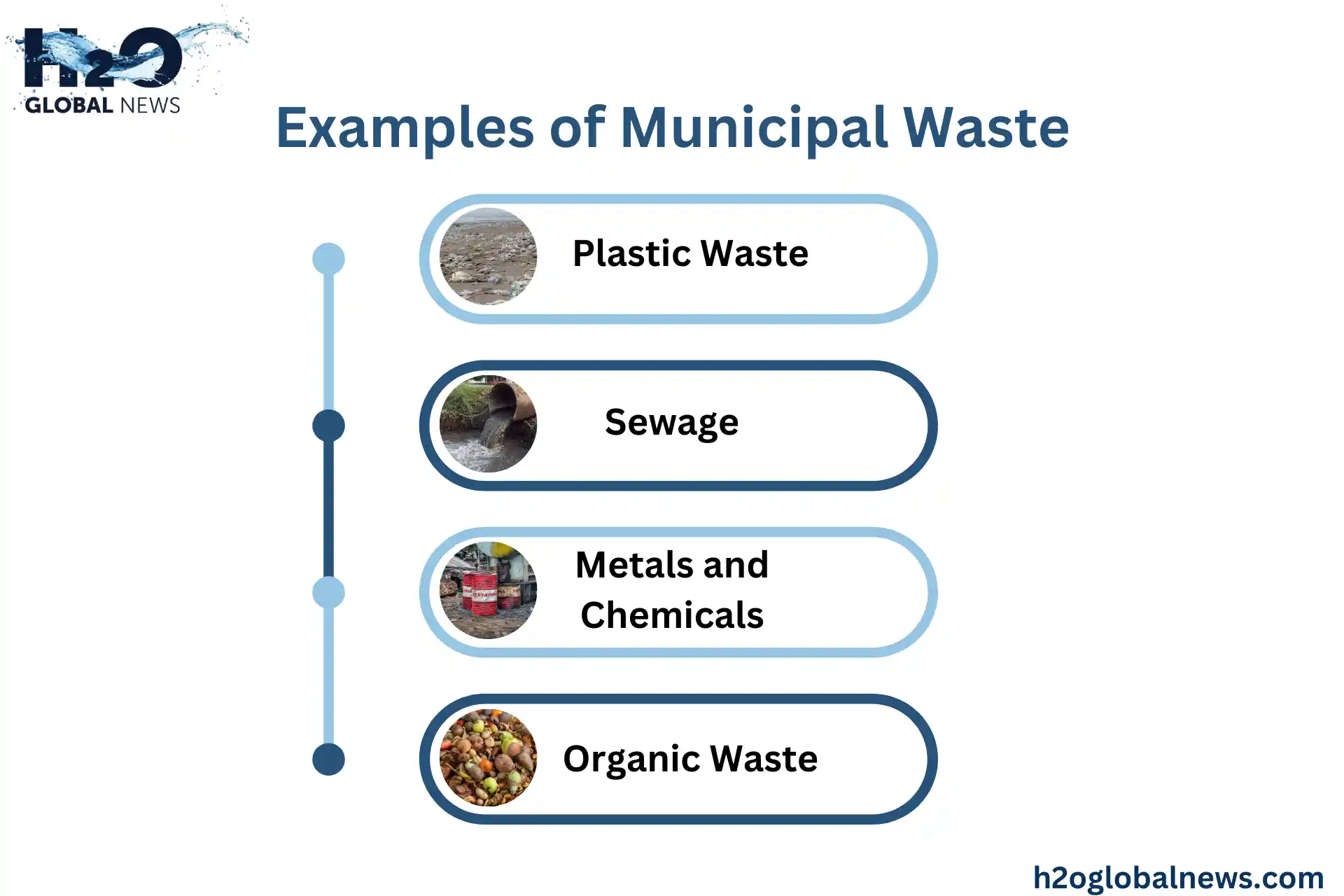
Examples of Municipal Waste and Its Impact
- Plastic Waste: Non-biodegradable and a significant contributor to the effects of trash on water.
- Sewage: Pathogens in untreated sewage can spread diseases through contaminated water.
- Metals and Chemicals: Metals and chemicals are found in industrial and household waste and poison aquatic life.
- Organic Waste: Contributes to oxygen depletion in water bodies.
Health Risks to Humans
The pollution of water bodies by municipal waste poses significant health risks to humans. Contaminated water can lead to various diseases and health conditions.
Waterborne Diseases
Exposure to contaminated water increases the risk of waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and hepatitis. These diseases are caused by pathogens present in polluted water and can spread rapidly, especially in communities with inadequate sanitation and healthcare infrastructure.
Chemical Exposure
Chemicals from municipal waste, including heavy metals and pesticides, can contaminate drinking water sources. Long-term exposure to these chemicals can lead to serious health issues, including cancer, neurological disorders, and reproductive problems. Vulnerable populations, such as children and pregnant women, are particularly at risk.
Food Safety Concerns
Water pollution affects not only drinking water but also food safety. Contaminated water used for irrigation can introduce harmful substances into crops. Seafood from polluted waters may contain high toxins, posing a consumer risk. Therefore, ensuring the safety of our water sources is essential for overall food safety.
The Environmental Impact
Municipal waste has a profound environmental impact on water bodies. The consequences extend beyond pollution, affecting ecosystems and biodiversity.
Aquatic Ecosystems
Water pollution disrupts aquatic ecosystems by introducing harmful substances that alter the natural balance. Nutrient pollution, caused by excess nitrogen and phosphorus from waste, leads to algal blooms. These blooms deplete oxygen levels in the water, creating ‘dead zones’ where aquatic life cannot survive. Additionally, toxic substances like heavy metals accumulate in the food chain, posing long-term risks to wildlife.
Biodiversity Loss
Polluted water bodies experience a significant decline in biodiversity. Species sensitive to water quality changes, such as certain fish and amphibians, are particularly vulnerable. The loss of these species can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem, reducing its resilience and ability to recover from disturbances.
Climate Change Connection
Municipal waste also contributes to climate change, indirectly affecting water quality. Decomposing organic waste in landfills produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Climate change exacerbates water pollution by increasing the frequency and intensity of storms, leading to more runoff and leachate production. Addressing municipal waste is crucial in mitigating climate change and its impact on water resources.
Solutions to Reduce Municipal Wastewater Pollution
1- Effective Waste Management Systems:
- Implement efficient waste management water strategies to prevent littering.
2- Community Awareness Programs:
- Educate citizens on the effects of trash on water and the importance of proper disposal.
3- Upgrading Infrastructure:
- Modernize sewage systems for better treatment of municipal wastewater.
4- Recycling and Reuse:
- Encourage recycling to reduce the volume of municipal waste entering water systems.

Conclusion
Municipal waste plays a significant role in water pollution, from untreated sewage to improper household trash disposal. By addressing issues in waste management water, promoting awareness about h2o waste disposal, and improving municipal wastewater treatment, we can reduce the environmental impact of municipal waste. Effective policies and community efforts are essential to protect our water resources for future generations.
FAQs
- How Can Water Waste Affect the Environment?
Water waste pollutes water bodies, harms aquatic life, and spreads diseases.
- Is Litter a Serious Problem for Water Bodies?
Yes, litter disrupts aquatic ecosystems and introduces harmful chemicals into the water.
- How Does Litter Affect Aquatic Ecosystems?
Litter can physically harm marine life, leach toxic chemicals, and disrupt natural habitats.
- What Does Municipal Water Mean?
Municipal water is water supplied by local government authorities for public use. It is sourced from natural bodies and treated to meet safety standards. Municipal water is used for drinking, cooking, cleaning, and sanitation.