Location: Western China
OEM: Beijing Beijiete (BGT)
Capacity: 12,000 tons Li2CO3/year
Est. Annual Cost Savings: $923,000 USD/year
Est. Annual Energy Savings: 18,461,000 kWh/year
The Challenge
Lithium and related compounds are essential for producing lithium-ion batteries, which are critical to power the energy transition. Lithium extraction and processing can be resource intensive, and a nanofiltration (NF)-based lithium extraction facility along the Zabuye Salt Lake in Western China, needed a solution to lower the energy consumption of nanofiltration for lithium separation.
The facility is located at a high altitude in a remote region, far from the local municipal power source. Because of these constraints, a concentrating solar power (CSP) station was designed and built for the facility. Due to high capital cost and footprint of the renewable CSP, the plant required an energy-efficient project design to save energy in order to reduce the capital expenses of the new power supply.
The Solution
Having previously partnered with Energy Recovery, Inc. on multiple wastewater projects, Beijing Beijiete (BGT), a public and leading company in water treatment technology in China, collaborated with the company once again to integrate PX® Pressure Exchanger® technology for its lithium extraction plant because of its proven capability to lower specific energy consumption (SEC) and maximum instantaneous power demand. The facility uses NF to concentrate lithium from brine and produce lithium bicarbonate, potassium chloride, and other valuable salts.

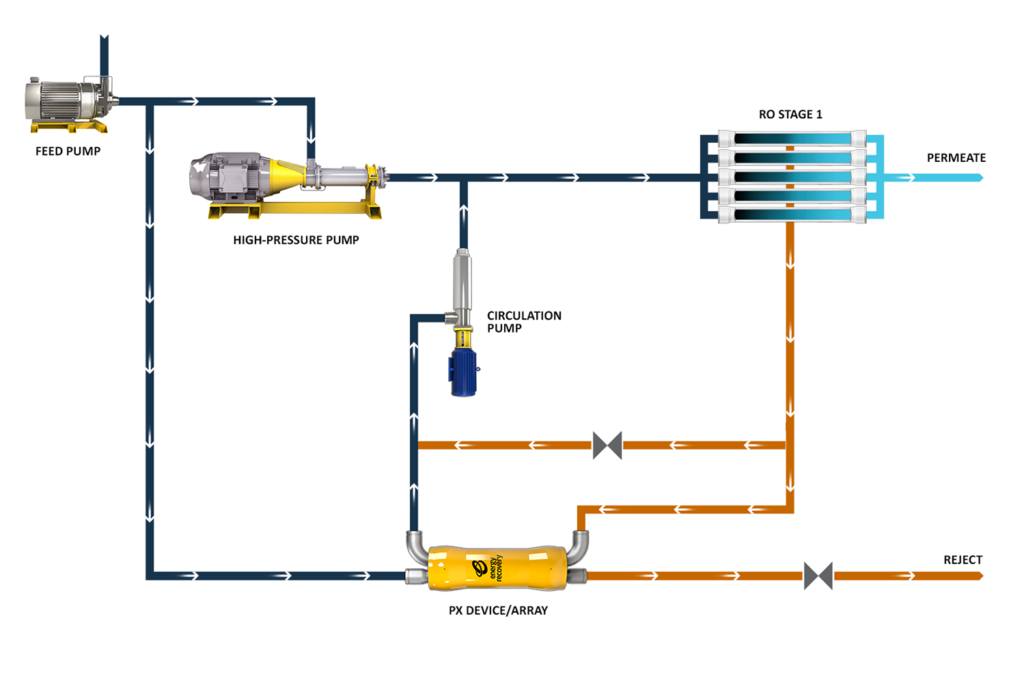
Nanofiltration-Based Lithium Extraction Facility Design:
- Five total NF stages, with the first stage utilizing two PX Q260s in each of the seven parallel trains
- Capable of producing 12,000 tons of lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) and 156,000 tons of potassium chloride (KCl) annually
- PX integration reduced the specific energy consumption to 3.4 kWh/m3, a reduction of approximately 57% compared to no ERD
The Result
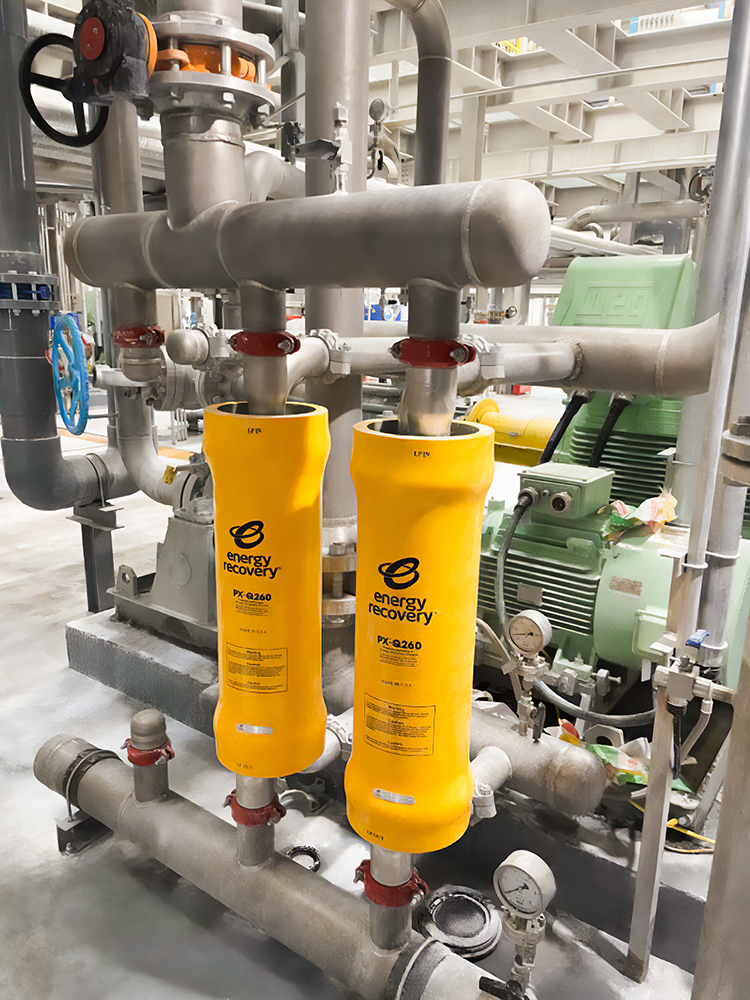

Using the PX not only helped to save energy costs but also reduced the number of solar panels and the amount of land needed for the CSP. Additionally, the PX reduced the overall power demand of the site, equivalent to ~6% of the size of the concentrated solar power plant, which has a capacity of 40 MW (“The World’s Highest,” 2024). Along with reduced energy consumption, the pressure exchanger provided a flexible and low-cost solution to recirculate brine flow and extend membrane life.







